Hi all,
just share aja nih untuk pengujian rugi2 trafo, semoga bermanfaat.
Jika trafo baru, maka pastinya sudah ditest seccara otomatis di pabrikan. namun jika ini perawatan atau perbaikan, maka tentu harusdiukur ulang.
Secara teori ada 3 losses yng harus diukur dan diukurnya pada kondisi NO LOAD, jadi tanpa beban. Ketiga loses itu adalah :
1. Iron losses at the core of the transformer, (rugi2 besi)
2. Dielectric losses at the insulating material and (rugi2 material isolasi)
3. The copper losses due to no-load current. (rugi2 tembaga)
Namun pada praktiknya, dua loses yang terakhir itu sangat kecil nilainya, jadi dalam pengukuran loses tanpa beban ini hanya akan diukur rugi2 besi nya saja.
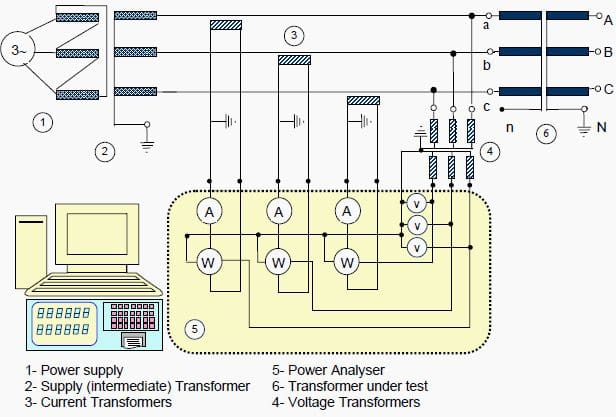
berikut konfigurasi pengukurannya :
Ini tambahan untuk total rugi2 ditambah rugi2 yang dihasilkan oleh eddy current nya :
During measurements, the supply voltage U´ is supplied to the transformer by the average value voltmeter. In this way, the foreseen induction is formed and as a result of this, the hysteresis losses are measured correctly. The eddy-current losses should be corrected according to equation below.
Pm = P0 · (P1 + k · P2)
Pm: Measured loss
P0: No-load losses where the voltage is sinusoidal
Here: P0 = Ph + PE = k1 · f + k2 · f2
k = [ U / U' ]2
P1: The hysteresis loss ratio in total losses (Ph) = k1 · f
P2: The eddy-curent loss ratio in total losses (PE) = k2 · f2
At 50 Hz and 60 Hz, in cold oriented sheet steel, P1 = P2 = % 50. So, the P0 no-load loss becomes:
Po = Pm / (P1 + k · P2) where P1 = P2 = 0,5
According to IEC 60076-1: Pm = P0 · (1 + d) where d = [ (U' - U) / U' ]












just share aja nih untuk pengujian rugi2 trafo, semoga bermanfaat.
Jika trafo baru, maka pastinya sudah ditest seccara otomatis di pabrikan. namun jika ini perawatan atau perbaikan, maka tentu harusdiukur ulang.
Secara teori ada 3 losses yng harus diukur dan diukurnya pada kondisi NO LOAD, jadi tanpa beban. Ketiga loses itu adalah :
1. Iron losses at the core of the transformer, (rugi2 besi)
2. Dielectric losses at the insulating material and (rugi2 material isolasi)
3. The copper losses due to no-load current. (rugi2 tembaga)
Namun pada praktiknya, dua loses yang terakhir itu sangat kecil nilainya, jadi dalam pengukuran loses tanpa beban ini hanya akan diukur rugi2 besi nya saja.
berikut konfigurasi pengukurannya :
Nah, ampere meter dan voltmeter itu lah nanti yang akan mengukur berapa daya yang diserap oleh trafo tersebut.
Ini tambahan untuk total rugi2 ditambah rugi2 yang dihasilkan oleh eddy current nya :
During measurements, the supply voltage U´ is supplied to the transformer by the average value voltmeter. In this way, the foreseen induction is formed and as a result of this, the hysteresis losses are measured correctly. The eddy-current losses should be corrected according to equation below.
Pm = P0 · (P1 + k · P2)
Pm: Measured loss
P0: No-load losses where the voltage is sinusoidal
Here: P0 = Ph + PE = k1 · f + k2 · f2
k = [ U / U' ]2
P1: The hysteresis loss ratio in total losses (Ph) = k1 · f
P2: The eddy-curent loss ratio in total losses (PE) = k2 · f2
At 50 Hz and 60 Hz, in cold oriented sheet steel, P1 = P2 = % 50. So, the P0 no-load loss becomes:
Po = Pm / (P1 + k · P2) where P1 = P2 = 0,5
According to IEC 60076-1: Pm = P0 · (1 + d) where d = [ (U' - U) / U' ]